AdaBoost Algorithm Explained .
Paper : A Decision-Theoretic Generalization of On-Line Learning and an Application to Boosting .
Authors : Yoav Freund and Robert E. Schapire .
Published in: AT6T Labs 1996 .
Before talking about AdaBoost we need to explain what is Boosting ?
Boosting is an ensemble meta-algorithm in supervised learning, and a family of machine learning algorithms that convert weak learners to strong ones. Boosting is based on the question posed by Kearns and Valiant [1] .
The Boosting technique is described as follows :
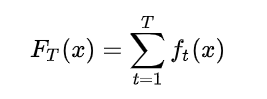
Where f_t is a weak classifier that takes a sample x as input and return the class of it , and T is the number of weak learners .
as you can see in the formula above , the Weak classifiers contribute to the final result with the same amount , this is exacly the difference between a simple Boosting algorithm and AdaBosst , in AdaBoost the weak learners contribute with a value conrespending to their performance .
The PseudoCode of AdaBoost is defined as following :
The Boosting technique is described as follows :

The Formula used to predict a certain sample is defined in the following :
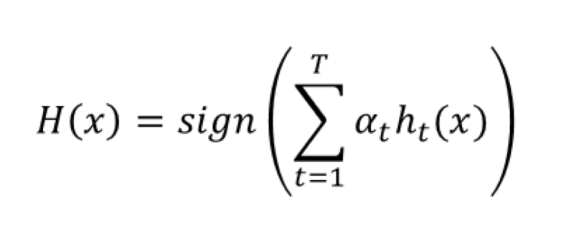
As you can see in the formula above every Weak classifier contribute to the result with a value corresponding to his performance , This is The difference between a simple Boosting algorithm and AdaBoost.
Implementation :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class DecisionStump:
def __init__(self):
self.classLabel = None
self.threshold = None
self.feature = None
self.alpha = None
def predict(self , x):
Feature = x[:,self.feature]
predictions = np.where(Feature < self.threshold , self.classLabel ,-1 * self.classLabel)
return predictions
class AdaBoost:
def __init__(self , nbr_classifiers = 10 , epsilon = 1e-10):
self.nbr_classifiers = nbr_classifiers
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.classifiers = []
def fit(self , x , y):
self.x_train = x
self.y_train = y
#Initialize The weights for all the samples with 1 / nbr_samples
self.weights = np.full(self.x_train.shape[0] , (1 / self.x_train.shape[0]) , dtype=np.float64)
def train(self ):
for i in range(self.nbr_classifiers):
Weak_Classifier_i = DecisionStump()
minimum_Error = float("inf")
#Iterate Over all the features to find the perfect one that will split our data
for feature in range(self.x_train.shape[1]):
current_Feature = self.x_train[:,feature]
#find thresholds Values which is the unique values of the feature that we're working with
thresholds = np.unique(current_Feature)
#iterate over all the thresholds to find the perfect one that will split the current feature
for threshold in thresholds:
"""
we don't know what the class of samples where feature < threshold , this is way we will test with class 1 ,
if the error more than 0.5 which is mean the majority of the samples that we calssified as 1 are -1 , so what we will do in this case ?
we will flip the error and assign -1 to our class label .
if error (label used is 1) = 0.8
then error(label is -1) = 0.2 .
"""
class_Label = 1
predictions = np.where(current_Feature < threshold , class_Label , -1 * class_Label)
error = np.sum(self.weights[self.y_train != predictions])
#flip The Error and The classLabel
if error > 0.5 :
error = 1-error
class_Label = -1
#if we find a better error less than the previous (we initialize The Error with float("if") which is a very small number)
if error < minimum_Error:
Weak_Classifier_i.classLabel = class_Label
Weak_Classifier_i.threshold = threshold
Weak_Classifier_i.feature = feature
minimum_Error = error
#Calculate The Performance of the Current Weak Classifier
Weak_Classifier_i.alpha = 0.5 * np.log((1 - minimum_Error + self.epsilon) / (minimum_Error + self.epsilon))
#Update The Weights
predictions = Weak_Classifier_i.predict(self.x_train)
self.weights *= (np.exp( - Weak_Classifier_i.alpha * predictions * self.y_train)) / (np.sum(self.weights))
#save our Weak Classifier
self.classifiers.append(Weak_Classifier_i)
def predict(self , x):
classifiers_predictions = [classifier.alpha * classifier.predict(x) for classifier in self.classifiers]
y_pred = np.sum(classifiers_predictions , axis = 0)
return np.sign(y_pred)
def plotTheModel(self):
fig , ax = plt.subplots()
Weak_Classifiers = []
Errors = []
for i in range(self.nbr_classifiers):
Weak_Classifiers.append("c"+str(i))
Errors.append(self.classifiers[i].alpha)
ax.bar(Weak_Classifiers , Errors)
ax.set_ylabel("Error")
ax.set_xlabel("classifiers")
ax.set_title("Error of classifiers")
plt.show()
#Test AdaBoost
```
#### Testing The Model :
```python
def Accuracy(y , y_hat):
return np.sum(y != y_hat) / len(y)
x , y = make_blobs(n_samples=500 , n_features=10 , centers=2 , random_state=0)
x_train , x_test , y_train , y_test = train_test_split(x , y , test_size=0.25)
adaBoost = AdaBoost()
adaBoost.fit(x_train, y_train)
adaBoost.train()
y_hat = adaBoost.predict(x_test)
print("AdaBoost Accuracy : ",Accuracy(y_test, y_hat))
adaBoost.plotTheModel()
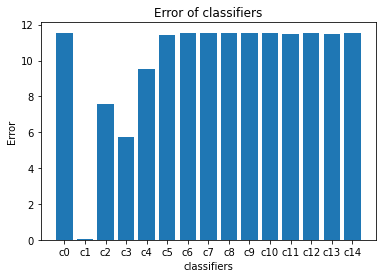
The Performance of each Weak Classifier that we get is :