K-Means Algorithm Explained .
History :
- The term “k-means” was first used by James MacQueen in 1967
- the idea goes back to Hugo Steinhaus in 1956.*The standard algorithm was first proposed by Stuart Lloyd of Bell Labs in 1957 ,it was not published as a journal article until 1982.
- In 1965, Edward W. Forgy published essentially the same method, which is why it is sometimes referred to as the Lloyd–Forgy algorithm.
Papers :
- MacQueen J.B 1967
- Steinhaus Hugo 1957 , Sur la division des corps matériels en parties
- Lloyd Stuart P 1957
- Forgy Edward W 1965
K-means is an unsupervised machine learning algorithm used for clustering .The idea behind K-means is very simple , we try to find similarities between the data so that , similar data points belongs to the same class.
Implementation :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
class KMeans:
def __init__(self , k , nbr_iterations = 500):
self.k = k
self.nbr_iterations = nbr_iterations
self.clusters = [[] for i in range(self.k)]
self.centers = []
def fit(self , x):
self.x = x
self.nbr_samples , self.nbr_features = x.shape
#initialize The Centers Randomly
centers_indexes = np.random.choice(self.nbr_samples , self.k , replace = False)
self.centers = [self.x[index] for index in centers_indexes]
for i in range(self.nbr_iterations):
#Assign Samples to the clossest Center
self.clusters = self.CreateClusters(self.centers)
oldCenters = self.centers
self.centers = self.UpdateCenters(self.clusters)
#Check if The Stoping Criteria is True
if self.StopingCriteria(oldCenters , self.centers):
break
def CreateClusters(self , centers):
CurrentClusters = [[] for i in range(self.k)]
for index , sample in enumerate(self.x):
clossestCenter = self.clossest_center(sample , centers)
CurrentClusters[clossestCenter].append(index)
return CurrentClusters
def clossest_center(self , sample , centers):
distances = [self.euclideanDistance(sample, center) for center in centers]
return np.argmin(distances)
def UpdateCenters(self , clusters):
newCenters = np.zeros((self.k , self.nbr_features))
for index , cluster in enumerate(clusters):
center = np.mean(self.x[cluster] , axis = 0)
newCenters[index] = center
return newCenters
def StopingCriteria(self , oldCenters , newCenters):
distances = [self.euclideanDistance(oldCenters[i], newCenters[i]) for i in range(self.k)]
return sum(distances) == 0
def getClusters(self):
labels = np.empty(self.nbr_samples)
for index , cluster in enumerate(self.clusters):
for sampleIndex in cluster:
labels[sampleIndex] = index
return labels
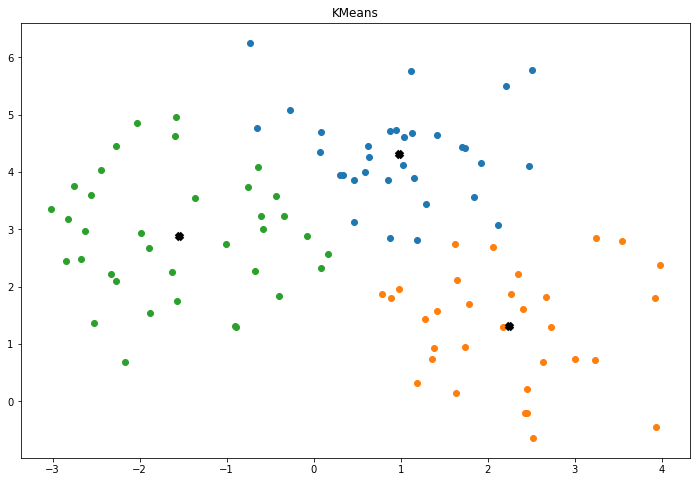
def displayTheResult(self):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))
#display The Clusters
for _ , index in enumerate(self.clusters):
points = self.x[index]
ax.scatter(points[:,0] , points[:,1])
#display The Centers
for center in self.centers:
ax.scatter(center[0] , center[1], marker="x", color="black", linewidth=5)
plt.title("KMeans")
plt.show()
def euclideanDistance(self , x1 , x2):
return np.sqrt(np.sum( (x1 - x2)**2 ))
Testing The Model :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def accuracy(y_true , y_pred):
return np.sum(y_true == y_pred) / len(y_true)
x , y = make_blobs(n_samples=100 , n_features=2 , centers=3 , random_state=0)
nbr_classes = len(np.unique(y))
K_means = KMeans(k = nbr_classes)
K_means.fit(x)
y_pred = K_means.getClusters()
K_means.displayTheResult()
print("KMeans Accuracy : ",accuracy(y, y_pred))
The Model Result :